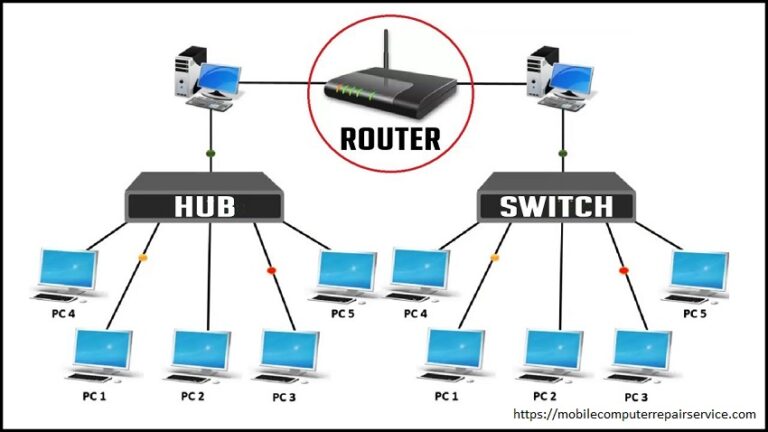
In an Ethernet network, their parts at different levels, for example, a Hub, a Switch, and a Router.
The elements of the three gadgets are on the whole very unique concerning each other, regardless of whether at times they are completely coordinated into a solitary gadget.
Because of that, numerous individuals feel befuddled about the contrasts between a hub, a switch, and a router.
The difference between a hub, a switch, and a router is many.
What Is the Difference Between a Hub, a Switch, and a Router?
Read the article to know about these in detail and to know the difference between a hub, a switch, and a router.
Hub
Hub is generally used to associate fragments of a LAN (Neighborhood). A hub contains different ports.
At the point when a bundle shows up at one port, it is duplicated to different ports so that all sections of the LAN can see all parcels. Hub goes about as a typical association point for gadgets in a network.
In a hub, a frame is passed along or “broadcast” to all of its ports. It doesn’t make any difference that the frame is just bound for one port.
The hub has no chance to get off recognizing which port a frame ought to be shipped off. Moreover, a 10/100Mbps center should impart its data transmission to all of its ports.
In correlation, a switch tracks the Macintosh (Media Access Control) locations of the relative multitude of gadgets associated with it. With this data, a network hub can recognize which framework is perched on which port.
So when an edge is gotten, it knows precisely which port to send it to, without fundamentally expanding network reaction times. What’s more, not normal for a center point, a 10/100Mbps switch will apportion an entire 10/100Mbps to every one of its ports.
So paying little mind to the laptops communicating, clients will consistently approach the greatest measure of data transfer capacity.
Features of Hub
Here, are significant highlights of hub which are:
- It works with broadcasting and shared transfer speed.
- It has 1 transmission area and 1 impact space
- Works at the actual layer of the OSI model
- A virtual LAN can’t be made utilizing a center
- Offers help for half-duplex transmission mode
- A hub has quite recently a solitary transmission space
- Doesn’t uphold spreading over tree convention
- Bundle impacts happen generally inside a center
Switch
A switch works at the information connect (layer 2) and now and then the network (layer 3) of the OSI (Open Frameworks Interconnection) Reference Model and along these lines uphold any bundle convention.
LANs that utilization changes to join sections are called exchanged LANs or, on account of Ethernet networks, exchanged Ethernet LANs. In networks, the switch is the gadget that channels and advances parcels between LAN portions.
Highlights of Switch
Here, are significant highlights of switch:
- It is Data Link layer gadget (Layer 2)
- It works with fixed data transmission
- It keeps a Macintosh address table
- Permits you to make virtual LAN
- It functions as a multi-port scaffold
- Supports half and full-duplex transmission modes
- Generally accompanies 24 to 48 ports
Router
A router is associated with in any event two networks, normally two LANs or WANs (Wide Territory networks) or a LAN and its ISP.s (Web access Provider.s) network.
The router is for the most part situated at passages, where at least two networks associate.
Utilizing headers and sending tables, the router decides the best way to advance the bundles.
Moreover, the router utilizes conventions, for example, ICMP (Web Control Message Convention) to speak with one another and designs the best course between any two hosts.
In a word, a router advances information bundles along with networks.
Ethernet-switch
In contrast to an Ethernet center point or switch that is worried about sending outlines, a switch is of course bundled to different networks until that parcel eventually arrives at its objective.
One of the critical highlights of a parcel is that it contains information as well as the objective location of where it’s going.
In addition, switch is the just one of these three gadgets that will permit you to share a solitary IP (Web Convention) address among numerous network customers.
Hub versus Switch versus Router
In network hardware and gadgets, information is normally sent as an edge. At the point frame is received, it is intensified and afterward communicated to the port of the objective (PC).
The huge distinction among hub and switch is in the technique where frames are being conveyed.
You can have a clear view of the comparison among hub vs switch vs router here:
| template | Hub | Switch | Router |
| Layer | Physical layer | Data link layer | Network layer |
| Function | To connect a network of personal computers together, they can be joined through a central hub | Allow connections to multiple devices, manage ports, manage VLAN security settings | Direct data in a network |
| Data Transmission form | electrical signal or bits | frame & packet | packet |
| Port | 4/12 ports | multi-port, usually between 4 and 48 | 2/4/5/8 ports |
| Transmission type | Frame flooding, unicast, multicast or broadcast | First broadcast, then unicast and/or multicast depends on the need | At Initial Level Broadcast then Uni-cast and multicast |
| Device type | Non-intelligent device | Intelligent device | Intelligent device |
| Used in(LAN, MAN, WAN) | LAN | LAN | LAN, MAN, WAN |
| Transmission mode | Half duplex | Half/Full duplex | Full duplex |
| Speed | 10Mbps | 10/100Mbps, 1Gbps | 1-100Mbps(wireless); 100Mbps-1Gbps(wired) |
| Address used for data transmission | MAC address | MAC address | IP address |
Conclusion
The understanding among hub, switch and router is a mistaking term for clients. People should know the difference between a hub, a switch, and a router.
Understanding these qualifications among them can be useful to locate the most fitting gadget for a network.
